If you’re new to running a website, you might be wondering, “What is a data controller?”
It’s a term that’s often thrown around in discussions about online data privacy, and it’s one that you, as someone responsible for managing user data, should definitely understand.
Your grasp of this concept is important for safeguarding personal information and ensuring your compliance with the law.
In this article, we’ll talk about data controllers and their critical responsibilities under the GDPR.
This way, you can confidently navigate GDPR requirements, protect user data, and build trust in the age of data privacy.
- Data controllers decide how personal data is used, with legal responsibilities under GDPR for transparency and consent.
- Data controllers make decisions, while data processors follow instructions. Controllers face legal obligations.
- Non-compliance risks fines, lawsuits, reputational damage, and regulatory investigations. GDPR compliance is essential for trust and business success.
Table of Contents
PRO TIP: Take the hassle of writing your own privacy policy away with our privacy policy generator trusted by over 200,000 businesses. It’ll save you hours of work and possible costly legal mistakes.
What Is a Data Controller Under the GDPR?
A data controller is an entity that determines the purposes and means of processing personal data.
Simply put, if you are in charge of collecting and using people’s personal data on your website, you’re a data controller.
Handling user data requires you to follow specific requirements to ensure data privacy and security, which is where GDPR comes in.
The General Data Protection Regulation is a set of rules designed to protect people’s personal information in the digital world.
What Are the Responsibilities of a Data Controller?
Understanding the role of a data controller and the GDPR is not only important for legal compliance but also for creating a positive relationship with your website’s users.
As a data controller, you shoulder several key responsibilities to ensure data protection and privacy. Here’s a concise list of your primary obligations:
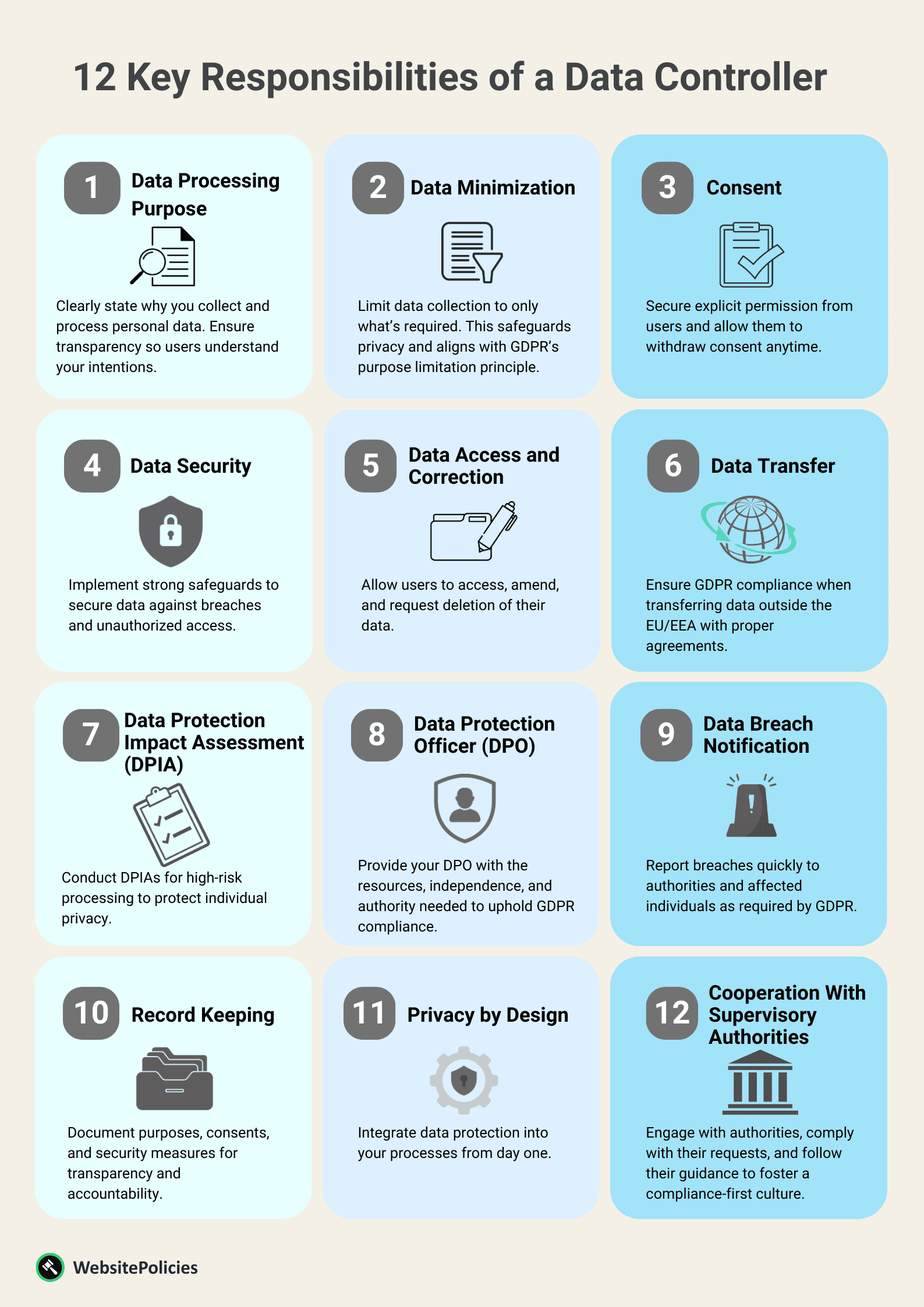
1. Data Processing Purpose
One of your primary obligations as a data controller is to transparently define and communicate the specific purposes for collecting and processing personal data.
Clarity in this regard is important to ensure individuals understand why their data is being used.
2. Data Minimization
Data minimization involves gathering only the essential information required for the intended purposes.
This practice ensures you avoid amassing excessive or irrelevant data, safeguarding users’ privacy and complying with the GDPR’s principles of data minimization and purpose limitation.
In my opinion, embracing data minimization isn’t just a legal requirement but a strategic advantage.
By keeping your data lean and focused, you are not only on the right side of the law but also building trust with your users.
3. Consent
Securing valid and explicit consent from users entails obtaining clear, affirmative permission before processing their data.
Equally important is granting them the ability to withdraw consent at any point in time. This helps them have control over their personal information, aligning with GDPR principles.
4. Data Security
Data security requires the implementation of strong protective measures.
These safeguards are important to preserve the confidentiality and integrity of the personal data you gather, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
PRO TIP: When you show a solid commitment to data security, you’re not just ticking GDPR boxes. You are genuinely demonstrating responsible data handling.
5. Data Access and Correction
Facilitating data access and correction involves providing users with the means to access their personal data, make necessary amendments, and request deletion when data is no longer relevant for the stated purposes.
It allows your website users to exercise control over their information in accordance with GDPR requirements.
6. Data Transfer
When transferring personal data outside the EU/EEA, a data controller’s responsibility is to adhere to GDPR requirements.
This includes implementing data transfer agreements or certifications to ensure that data is adequately protected.
Doing this ensures the users’ privacy and that you’re complying with international data transfer regulations.
7. Data Protection Impact Assessment
Data controllers are obligated to conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for high-risk data processing activities.
DPIAs are tools that help you evaluate the potential impact on individuals’ privacy.
8. Data Protection Officer (DPO)
If GDPR mandates it, you will need to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO). You also need to provide the DPO with the essential resources to effectively fulfill their duties.
This includes expertise, independence, and support, ensuring your website’s compliance with data protection regulations and safeguarding the users’ privacy.
9. Data Breach Notification
In case of a data breach, it is your responsibility to notify the supervisory authority and the affected individuals within the specified time frames as required by the GDPR.
This timely response upholds transparency, aids in mitigation, and complies with data breach notification obligations.
10. Record Keeping
By diligent record-keeping, you ensure transparency, accountability, and compliance with GDPR standards.
These records should include the purposes for data collection, details of consent, and the security measures in place.
11. Privacy by Design
Adopting a “Privacy by Design” approach means embedding data protection into your business processes and services right from the beginning.
In doing so, you fortify data security, promote compliance with GDPR principles, and enhance user trust.
12. Cooperation With Supervisory Authorities
Effective collaboration with data protection authorities involves actively engaging with these authorities, complying with their requests, and heeding their recommendations.
This cooperative approach is important for creating a culture of compliance.
What Are Joint Data Controllers?
Joint data controllers are entities that, under the GDPR, jointly determine the purposes and means of processing personal data.
In practical terms, this often means multiple organizations collaborating in data processing activities with shared responsibilities.
When operating as joint data controllers, businesses share the obligations outlined by the GDPR. These include:
- Data Processing Agreement: Establish a clear data processing agreement between the joint controllers that outlines their respective responsibilities, ensuring compliance and accountability. For instance, if two e-commerce companies collaborate on a joint marketing campaign, they should define their roles and responsibilities in processing customer data.
- Transparency: Joint controllers must collectively inform individuals about their roles, how data is processed, and the purpose of processing, emphasizing transparency. For example, two research institutions working on data analytics should provide clear, shared information about their data processing activities.
- Data Subject Rights: Facilitate the exercise of data subject rights and respond to their requests, including those related to access, rectification, and erasure. In the case of two businesses sharing a CRM system, both should be prepared to handle data subject requests.
- Data Security: Implement strong security measures to protect the shared personal data from breaches or unauthorized access.
- Data Breach Notification: Collaborate in reporting data breaches to the supervisory authority and affected individuals within the specified time frames. So, if a data breach occurs during the joint marketing campaign, both businesses must work together to fulfill their notification obligations.
- Record Keeping: Maintain comprehensive records of data processing activities that involve shared responsibilities. This record-keeping becomes critical for ensuring compliance in all joint data processing scenarios.
To determine if your business is functioning as a joint data controller, ask these questions:
- Do you have a shared objective with other companies for the data processing? For instance, collaborating on a marketing campaign that involves sharing customer data for joint promotions.
- Are you processing the data for the same reason as another data controller? If you and another organization are both using customer data for marketing purposes, you might be joint controllers.
- Are you using the same set of personal data for the processing as another data controller? This could involve both entities utilizing a common database for data processing.
- Are you designing the data processing with another data controller? For example, if you and another organization are jointly creating a data analytics platform that uses shared data, you likely fall into the category of joint data controllers.
Differences Between Data Controllers and Processors
It’s important to understand the difference between data controllers and data processors. This understanding forms the bedrock of a well-structured and legally compliant data management system.
Data controllers take the lead in deciding why and how personal data is processed. They shape the purposes and methods of handling this data, assuming the primary responsibility for it. Think of them as the captains of the ship, steering the course.
Data processors, on the other hand, play an important role in the data journey. They’re the ones who carry out the data processing tasks, but they do so under the direct guidance and instructions of the data controller. They have their own specific duties laid out in the GDPR.
These responsibilities include various aspects, such as ensuring that personal data remains secure, maintaining confidentiality, and strictly processing data in line with the data controller’s directions.
In essence, data processors are like the crew members, executing tasks based on the captain’s orders.
By knowing these distinctions, businesses can effectively allocate roles and responsibilities, ensuring that personal data is treated with care, security, and in full compliance with the GDPR.
Possible Legal Implications for Data Controllers
As a data controller, you’ve got a long list of responsibilities. Wondering what can happen if you don’t play by the rules?
First up, you could be hit with hefty fines under GDPR, which could go as high as €20 million or 4% of your annual global turnover, whichever stings more.
Individuals whose data you’re responsible for can also take you to court if you mess up and violate their rights. That can lead to lawsuits and potential compensation payouts.
It’s not just about money. Your reputation takes a hit, too.
Privacy mishaps and data breaches can tarnish your image, resulting in bad press and a loss of trust. This can affect your relationships with customers and partners.
On top of that, you might face regulatory investigations, diverting your focus from your core business.
If there’s a data breach, you are legally obliged to inform the authorities and affected individuals promptly. Failing to do so can get you into trouble.
PRO TIP: Being on the right side of data protection is not just a legal obligation. It’s actually a smart business move. Remember, it’s not just about the law. It’s about trust, reputation, and doing right by your users.
Who Is Considered a Data Controller?
Still unsure who qualifies as a data controller? Let’s shed some light on this concept by exploring some typical businesses and entities that fall into this category:
- E-commerce Websites: If you run an online store, you’re a data controller because you determine how customer information is used. This includes order processing and personalized product recommendations.
- Social Media Platforms: If you operate a social networking site, you fall into this category. You collect user data for advertising and friend recommendations, and you decide how that data is utilized.
- Marketing Agencies: When you run a marketing agency, you control the data used for ads and campaigns, dictating how you reach potential customers on behalf of your clients.
- Subscription Services: If you offer subscription-based services, like streaming platforms, you are a data controller. You collect user data to tailor content recommendations and handle billing.
- Data Analytics Companies: Firms specializing in data analysis are also data controllers. They collect data to provide insights to other businesses and set the rules for data usage.
Is Your Business a Data Controller?
To determine if your business is a data controller, consider your level of control over personal data. If you collect, use, and make decisions about users’ data, you likely qualify as a data controller.
Key factors include defining the purposes for data processing, obtaining consent, and setting the methods for data handling.
If you interact directly with data subjects, maintain records of processing activities, and hold responsibility for data security, you’re fulfilling the role of a data controller.
Essentially, if you are the one steering the ship when it comes to personal data, your business is a data controller, so GDPR and data protection rules apply.
Data Controller Self-Assessment Questionnaire
Here’s a set of questions you can use to determine if your business falls under the category of data controllers:
- Did your organization independently decide to initiate the collection and processing of personal user data?
- Has your organization set the specific purposes for processing the data?
- Did your organization make the choices regarding the types of personal data to be gathered?
- Will your organization derive any commercial benefits from the processing of this data, aside from payment for controller services?
- Do the data subjects include individuals who are your own employees?
- Were the determinations about the affected users made by your organization as part of or due to the data processing?
- Is your organization exercising its professional judgment when handling personal data?
- Does your organization maintain direct communication and interaction with the data subjects?
- Is your organization solely responsible for deciding how the data is processed?
- Has your organization outsourced data processors to handle the data?
Answering “yes” to these questions implies that your business operates as a data controller, taking charge of decisions related to personal data collection and processing.
This self-assessment can help ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Tips to Ensure GDPR Compliance as a Data Controller
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) places significant responsibilities on data controllers. While it may seem like a daunting task, ensuring GDPR compliance is manageable with the right approach.
Here are some practical tips to help you navigate this complex landscape.
1. Understand Your Data
Get to know your data inside out. Identify what personal data you’re collecting, where it is stored, and how it is used. The better you understand your data, the easier it is to protect it.
2. Prioritize Data Security
Safeguarding personal data should be your top priority.
Implement strong security measures, conduct regular security assessments, and make sure your team is well-trained in data security best practices.
3. Transparency Is Key
Be crystal clear with site users and visitors about how their data is used.
Draft concise and comprehensible privacy policies, use easy-to-understand language, and keep data subjects informed about their rights.
In an age where personal data is an increasingly valuable commodity, I believe that being transparent about your data practices is a testament to your commitment to respect and protect the privacy of your users.
It sets the foundation for a trustworthy and enduring relationship between your business and its clientele.
4. Consent Management
Double-check that you obtain valid consent before processing data and make it easy for users to withdraw consent. Plus, remember to document all consent records.
5. Data Subject Rights
Respect data subject rights. Be responsive to data subject requests, including access, rectification, and erasure.
Establish a clear process for handling these requests and adhere to the specified timeframes.
By following these tips, you not only protect personal data but also demonstrate your commitment to privacy and responsible data handling.
Remember, GDPR is here to stay, and embracing it is a smart move for your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a data controller under GDPR?
A data controller determines how personal data is processed. If you collect and use personal data, you are a data controller.
What are the primary responsibilities of a data controller?
Data controllers must define data processing purposes, minimize data, obtain consent, ensure data security, allow data access, and more.
How do joint data controllers differ from individual data controllers?
Joint data controllers collaborate in data processing, sharing responsibilities. They must agree on data processing terms and ensure transparency.
What separates data controllers from data processors under GDPR?
Data controllers make decisions about data use, while data processors follow instructions. Controllers bear more legal responsibilities.
What are the legal implications for data controllers who don’t comply with GDPR?
Non-compliance can lead to regulatory fines, lawsuits, reputational damage, and regulatory investigations. Compliance is important for trust and business success.
Who qualifies as a data controller in various businesses?
E-commerce sites, social media platforms, healthcare providers, financial institutions, and more act as data controllers depending on their data management.
How can I determine if my business is a data controller?
If you control personal data collection, use, and decision-making, you likely qualify. Self-assessment can confirm your role.
What tips can help ensure GDPR compliance as a data controller?
Understand your data, prioritize security, ensure transparency, manage consent, respect data subject rights, and document processes to demonstrate commitment to privacy.



