The increasing amount of data breaches and privacy scandals have heightened data privacy awareness, prompting governments worldwide to enact stringent regulations to safeguard individuals’ data rights.
Through binding legislation or an emphasis on ethical responsibility, many data privacy laws have mandated or suggested the appointment of a Data Protection Officer for comprehensive data protection measures to take place successfully.
In this guide, we’ll explore the role and significance of data protection officers in the context of online businesses, their responsibilities, the legal requirements for having one, and best practices for hiring the right one for your business.
- The DPO’s role is to ensure data protection compliance, act as a liaison with regulators, and advise organizations to avoid data leaks, breaches, and mishandling of private information.
- DPOs are legally required in specific cases, like large-scale data processing or sensitive data handling.
- Effective DPOs have legal expertise, uphold ethics, communicate well, mitigate risks, stay updated, act independently, and maintain detailed records.
Table of Contents
PRO TIP: Take the hassle of writing your own privacy policy away with our privacy policy generator trusted by over 200,000 businesses. It’ll save you hours of work and possible costly legal mistakes.
What Is a Data Protection Officer (DPO)?
A Data Protection Officer, often called a DPO, is a designated individual within an organization responsible for overseeing data protection and privacy matters. Their primary role is to ensure that the organization complies with data protection laws and regulations and to safeguard the privacy of their consumers.
The necessity for a DPO depends on factors like the nature of data processing activities and applicable laws. For example, the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates a DPO for public bodies, large-scale monitoring, or processing of special data categories.
While not every business is legally required to appoint a DPO, the benefits of having one extend beyond mere GDPR compliance. By overseeing compliance efforts and facilitating communication between the organization, data subjects, and regulatory authorities, a DPO helps build trust and transparency in data handling practices and your business.
According to Article 38 of the European Data Protection Regulation, the DPO should be an onlooker and an active participant in ensuring that your organization adheres to data protection regulations. Their involvement in all matters of personal data is of utmost importance.
Moreover, it’s important to understand that the DPO must remain independent and free from external influence. They should not receive instructions that could compromise their ability to safeguard personal data and uphold privacy rights. This independence ensures that the DPO can act objectively and without bias.
While the primary role of the DPO is to oversee data protection, they may also have other tasks and duties within your organization. However, these additional responsibilities mustn’t create conflicts of interest that could compromise their core data protection duties.
PRO TIP: DPOs are bound by secrecy and confidentiality regarding the performance of their tasks. This ensures that sensitive data remains secure and privacy rights are respected.
What Does a DPO Do?
A DPO’s role is multifaceted, combining advisory, monitoring, supervisory, and compliance activities. They are instrumental in building a data protection culture within an organization and ensuring that it operates in full alignment with data privacy laws and ethical standards.
Let’s explore the specific responsibilities of a DPO as outlined in Article 39 of the EU GDPR.
- Inform and Advise: One of the primary responsibilities of a DPO is to inform and suggest to your organization and your employees about your obligations to comply with data protection laws. This involves providing guidance on handling personal data, and ensuring that everyone within your organization knows your internal data protection policies.
- Monitor Compliance: DPOs play a central role in monitoring compliance with relevant data privacy and protection laws. This includes managing internal data protection activities, raising awareness of data protection issues, conducting training for staff members, raising awareness, and performing internal audits.
- Reviewing Privacy Policies: DPOs ensure that your privacy statement aligns with current regulations and best practices. They also ensure that any changes in data processing activities or new regulations are promptly reflected in the privacy policy. It’s important to note that while the DPO provides guidance and oversight, the actual drafting of the privacy policy can be done by other professionals.
- Advise on Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): DPIAs systematically assess data processing activities to identify and mitigate privacy risks. DPOs recommend the need for DPIAs and monitor their implementation. They help assess the potential impact on individuals’ privacy and ensure appropriate measures are taken to mitigate risks.
- Cooperate with Regulatory Authorities: DPOs are a significant link between your business and the relevant regulatory authorities overseeing data protection laws. They cooperate with these authorities by handling communications, inquiries, and notifications related to data protection matters.
- First Point of Contact: DPOs act as regulatory bodies’ first point of contact. This means that in the event of data breaches or other data protection incidents, the DPO is responsible for initiating contact with the regulatory authority and coordinating your organization’s response.
- Responding to Data Subjects: DPOs also serve as a direct point of contact for individuals whose personal information is being processed. This accessible communication channel allows data subjects or your customers to reach out and voice their concerns, seek clarifications, or request action related to their personal data.
- Risk Assessment: DPOs continuously evaluate and reevaluate the risks associated with data processing, adapting to technological changes, regulations, and your organization’s operations.
- Maintain Records of Processing Operations: This involves documenting the details of data processing activities within your organization, including the types of data processed, the purposes of processing, and the security measures in place.
Who Needs to Appoint a DPO and Why?
One of the primary reasons to have a DPO is legal compliance. Several data protection laws, most notably the European Union’s GDPR, mandate the appointment of a DPO as a data protection authority under specific circumstances.
According to Article 37 of the GDPR, any organization processing the personal data of EU residents must designate a DPO in certain specific cases:
- Public Authorities: Public authorities or bodies (excluding courts acting in their judicial capacity) must appoint a DPO. This includes government agencies, local authorities, and public organizations. These entities handle significant amounts of personal and organizational data, often related to citizens’ interactions with government services, making the appointment of a DPO mandatory.
- Large-Scale Monitoring: If your organization’s primary operations include the extensive and systematic monitoring of personal data on a “large scale,” a DPO is required. This applies to scenarios where data processing is continuous and extensive, such as tracking online behavior for targeted advertising or monitoring network activities for optimization, like in telecommunications, e-commerce, and social media.
- Processing Special Categories of Data: If the core activities consist of large-scale processing of special categories of data or personal data related to criminal convictions and offenses, appointing a DPO is non-negotiable. Healthcare organizations often process sensitive medical information, which falls under the category of special categories of data (sometimes referred to as sensitive data), including patient medical records, genetic information, or data related to an individual’s health.
Legal requirements are not limited to the European Union. Many countries have introduced similar data protection laws that necessitate the appointment of a DPO, such as Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), which requires organizations to appoint a Privacy Officer.
The DPO shall ensure better information security of your company’s data through systematic monitoring of data subjects and consistent data protection compliance within the specific legal framework, reducing the likelihood of data leaks and breaches.
Am I Legally Required to Fill the DPO Role?
According to the EU GDPR’s Article 37 and mandates by the UK GDPR, you are legally required to appoint someone to fulfill the role of the data protection officer (DPO) if you are a public authority, your core activities involve large-scale systematic monitoring, or you process special or sensitive categories of data at scale.
Exemptions include small businesses where the organization’s compliance is not essential due to the low volume of data they are handling. However, even if not mandatory, legislation usually emphasizes ethical responsibility for any organization involved in data collection.
How Much Does a DPO Cost?
Understanding the financial implications of appointing a Data Protection Officer is crucial to compliance with data protection regulations. Whether you hire a full-time employee or outsource the role, it’s essential to consider the associated costs and benefits.
Hiring a Full-Time for the DPO Role
One of the most significant costs of hiring an in-house DPO is their salary and benefits. DPOs are typically professionals with expertise in data protection laws and practices. The salary can vary significantly based on factors such as the DPO’s qualifications, experience, and the location of your business.
Hiring an experienced DPO may sometimes require a substantial financial commitment. According to Zip Recruiter, the average hourly salary of DPOs in the United States is around $22 and can go as high as $32.
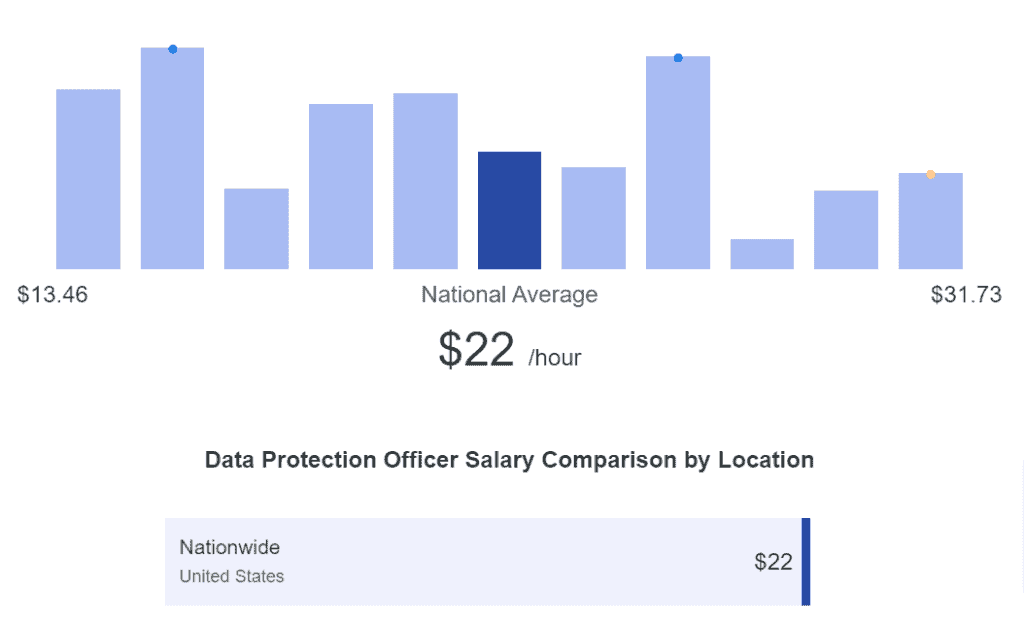
You may also need to invest in ongoing training and certification for your DPO to ensure they have the knowledge and expertise necessary to fulfill their role effectively. Data protection laws evolve, and staying up-to-date with the latest regulations and best practices passed by the relevant supervisory authorities is crucial.
PRO TIP: To perform their duties efficiently, DPOs may require specific tools and resources. This could include data subject access request forms, data protection management software, cybersecurity tools, and communication platforms to engage stakeholders.
Outsourcing the DPO Role
Outsourcing the DPO role can offer cost advantages since you won’t have the ongoing benefit expenses associated with a full-time employee. Instead, you typically pay a fee to the external DPO provider.
Additionally, outsourced DPO services often come with a team of experts who have experience across various industries and compliance scenarios. This can provide a broader and deeper knowledge base than an in-house DPO.
Outsourcing allows you to scale your data protection efforts as needed. You can adjust the level of service to match your organization’s size and complexity without the challenges of hiring or dismissing full-time employees.
External DPO providers can also offer flexibility in terms of engagement models. You can choose between retainer-based services, project-based support, or periodic assessments based on your specific requirements.
Additional Considerations
The cost of non-compliance with data protection regulations can be significantly higher than the investment to ensure that the data protection measures are fully implemented by hiring a DPO. Fines and penalties for breaches can be substantial, making DPO services a prudent investment.
DPOs’ role as information controllers and data protectors helps identify and mitigate data protection risks, preventing costly data breaches and legal consequences and enhancing trust in customers, partners, and stakeholders.
Effective DPO’s Qualifications
Appointing the Data Protection Officer is essential to ensure compliance with data privacy law within your organization. An effective DPO possesses professional qualities that enable them to navigate the complex data protection landscape. Here’s a list of qualifications that define an effective DPO:
- Expert Knowledge of Data Protection Laws and Regulations: Your DPO should have a solid grasp of data protection laws, like the GDPR, and applicable rules to your business. They should also keep up with changes in privacy laws to ensure your business stays compliant.
- Strong Legal and Compliance Background: Look for a DPO with a legal or compliance work background. They should be skilled at understanding and applying complex legal rules to your business.
- Ethical and Integrity Standards: Your DPO must commit to upholding the highest ethical standards, as the DPO deals with sensitive personal data and privacy rights. The DPO should be someone your team can always trust and rely on.
- Communication and Education Skills: A good DPO needs to communicate effectively. They should be able to explain data protection rules clearly to you and your employees, no matter how complex the laws are.
- Risk Assessment Abilities: Your DPO should be good at spotting and mitigating data protection risks in your business operations.
- Problem-solving skills: DPOs need to be skilled in identifying compliance challenges and developing practical solutions. They should also be able to address data breaches or issues promptly to avoid further damage to your organization.
- Technological Awareness: A DPO must be familiar with emerging technologies and their implications for data protection. They should also have a solid understanding of cybersecurity principles to assess and enhance data security measures for your business.
- Adaptability and Continuous Learning: A good DPO should be willing to stay updated with evolving data protection trends, technologies, and legal developments to adjust your data protection strategy as the rules evolve.
- Independence and Objectivity: Your DPO should make decisions without being influenced by others in the company. They should be able to act independently and objectively, free from conflicts of interest, and avoid undue influence from management when making data protection-related decisions.
- Record-Keeping and Documentation Skills: An effective DPO should also have exceptional attention to detail, especially in maintaining records of data processing operations and compliance activities. Keeping comprehensive documentation to demonstrate compliance with regulatory authorities.
Best Practices for Hiring a DPO
Hiring a Data Protection Officer is a significant step in ensuring your company’s compliance with data privacy laws. I’ve seen many businesses make the mistake of rushing this process, only to regret it later. Here are some best practices I recommend:
- Experience Matters: Look for candidates with a strong background in data protection and privacy laws. It’s not just about knowing the laws but understanding how they apply to your location and your specific industry.
- Independence is Key: Your DPO should have the autonomy to perform their duties without any conflicts of interest. This means they shouldn’t have other roles within the company that could compromise their judgment.
- Continuous Training: Data privacy laws are ever-evolving. Ensure that your DPO is committed to ongoing education to stay updated with the latest changes and best practices.
- Communication Skills: Your DPO will be interacting with various departments and possibly external regulators. They need to communicate complex topics clearly and effectively.
- Technical Know-How: While they don’t need to be IT experts, a good DPO should have a basic understanding of your company’s technical infrastructure. This will help them identify potential vulnerabilities and work with IT to address them.
Remember, every business is unique, and your DPO’s responsibilities should align with your specific data processing activities and needs. You need to consider the volume and sensitivity of the data you handle and the complexity of your data processing operations.
The right DPO can be an incredible asset for your company. Take your time, do your research, and make an informed decision.



