In the digital age, where everything’s connected online, handling data the right way is a big deal. If you’re running a small online business, you’ve probably heard about Data Subject Access Requests or DSARs.
DSARs are like a window into the world of data privacy – a way for individuals to ask, “Hey, what do you know about me?” DSARs allow your customers to take control of their personal information, and understanding how to respond to them is important.
In this guide, I’ll explain DSARs and why they matter for your business. I’ll also give you the know-how to handle DSARs with confidence, including the steps to respond effectively and the challenges you might encounter along the way.
Table of Contents
PRO TIP: Take the hassle of writing your own privacy policy away with our privacy policy generator trusted by over 200,000 businesses. It’ll save you hours of work and possible costly legal mistakes.
What Is a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR)?
A Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) is a formal request made by an individual, the data subject, to an organization or company to provide information on the personal data that is being held or processed about them.
In simple terms, DSAR acts as a digital key your customers hold. They have a right to know what data you have about them, and DSARs are their way of asking for that info. And guess what? You’ve got to show them the goods.
DSARs put you in the spotlight for being open, honest, and respectful about data collection. But, it’s not just about playing nice. DSARs are also a legal requirement in many places.
For instance, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the ultimate rulebook for data protection. It grants several privacy rights, including the right to access, correct, delete, and restrict personal data. While GDPR originated in the European Union (EU), it extends its influence to any organization that collects or targets data concerning individuals in the EU.
In the USA, specifically California, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and its big sibling, the California Privacy Rights and Enforcement Act (CPRA), give customers the right to ask about their data, too. They’re all about putting the control back in the hands of the people whose data you’re handling.
CCPA provides California consumers with the following rights:
- To be informed about the collection, usage, and sharing of their personal data by businesses
- To request the deletion of their personal data (with certain exceptions)
- To opt out of the sale or sharing of their personal data
- To be protected from discrimination for exercising their CCPA rights
With the CPRA, consumers are further given the right to correct inaccuracies in their personal data held by businesses and control the usage and disclosure of sensitive personal information collected about them.
PRO TIP: Consider going the extra mile by not only fulfilling DSARs but also proactively informing customers about their data usage periodically. By doing so, you can build trust and demonstrate your commitment to data transparency.
DSAR vs DSR
DSAR is a specific formal request made by a user to an organization to obtain information on the personal data about them that is being held or processed. On the other hand, Data Subject Request (DSR) is a broader term that includes various rights individuals have under data privacy laws.
For example, the rights to access, rectify, erase, restrict, transfer, or object to the processing of their personal data.
Essentially, while DSAR focuses solely on accessing personal data, DSR includes a wider range of rights related to personal information protection. DSRs are like a bundle deal. They include not just the right of access (that’s the DSAR part), but also a bunch of other rights. Think of DSRs as a package deal with extras.
So, while DSARs are the stars of the show when it comes to asking for data, DSRs bring in the VIP treatment. They can involve data deletion requests, fixing incorrect info, and even objecting to how you’re using their data.
Common DSAR Types
Data subject access requests come in different types, each serving a specific purpose. Let’s break them down so you know exactly what to expect and how to handle them like a pro.
Request for Summaries
Imagine you’re giving your customers a quick overview of their data experience with your business. That’s what a request for a summary is all about. Your customers might want a concise rundown of what personal data you’ve got on them and how you’re using it. It’s giving them a chance to see your data file on them without diving into the details.
Request for Deletion
Sometimes, customers want a fresh start. A request for deletion means they’re asking you to wipe out their personal info from your records. They’re essentially hitting the reset button on their data relationship with your business. However, this doesn’t apply if you’ve got legal reasons to hold onto their data.
Request for Correction
Nobody’s perfect, and neither is data. A request for correction is when customers spot errors in their personal info. They’re reaching out to you to fix those glitches and make sure their data is accurate and up-to-date.
Even though customers can reach out manually, it’s best to make sure your website or app allows customers to edit their information on their own. It’ll be much easier for them and for you.
Request to Opt-Out of Sharing or Sale
Privacy matters and some customers might not want their data to be part of the sharing or selling game. A request to opt-out is them telling you to keep their data close and not share or sell it to third parties. It safeguards their data from being passed around.
PRO TIP: Offer clear instructions and include a dedicated section on your website outlining how a person can submit a DSAR. A user-friendly guide can make the process smoother for requesters.
DSAR Example
Here’s an example of a typical DSAR request businesses may receive from their customers:

If you collect any information from your users, you should be ready for these kinds of requests and respond to them promptly.
You can make the process of managing DSARs easier by using a compliant and automated DSAR form which you would usually link to in your privacy policy.
Who Can Submit a DSAR?
Most data privacy laws allow any consumer to submit a request to have access to their personal information, to modify or delete it.
This means that DSARs are open for submission by any person whose personal data is being processed by an organization. Customers, former ones, employees, and legal representatives all have a place in this lineup.
Let’s break it down so you know exactly who can submit these requests and why.
Customers
First up, the obvious one – your customers. They’re the ones who’ve shared their data with your business. It’s their personal info on the line, so naturally, they have the right to ask about it. Whether they’re curious about what you know or they want to exercise their privacy rights, customers are front and center in the DSAR game.
Former Customers and Users
Even if someone used to be a customer or user of your services, they still have a ticket to the DSAR party. If you’ve collected their data during their time with you, they can still request to know what’s in your data vault. It’s all about keeping things fair and transparent, no matter how long their data relationship lasts.
Employees
If you’ve got employees, they’re part of the DSAR club as well. Just like you’d want to know what data a company holds about you, your employees have the same subject rights. From payroll details to performance reviews, they can request a peek at the data you’ve got on them.
Legal Representatives
Sometimes, people can’t manage their own affairs. In such cases, legal representatives, like guardians or power of attorney holders, can step in and request DSARs on behalf of individuals who can’t do it themselves. This makes sure everyone’s rights are respected, even in challenging situations.
Warning: You should verify the identity of the person or that they have proper permission to ask for the data before you process the request. It’s their job to provide sufficient proof.
Who Can Respond to a DSAR?
When it comes to responding to data subject access requests, it’s a team effort, not a solo act. It’s all about collaboration between different departments, from legal to IT to customer support. Each team brings their expertise to the table to ensure a seamless and compliant DSAR process.
Here are the roles and responsibilities of the key players involved in the DSAR process.
Your Data Protection Officer (DPO)
If your business has a Data Protection Officer (DPO), they’re in the front seat when it comes to handling DSARs. Their role is to oversee data privacy and ensure your business follows the rules. When a DSAR lands on your doorstep, your DPO is the go-to person to coordinate and guide the response.
Your Privacy Team
You may set up a dedicated privacy-savvy team. This could include legal experts, compliance officers, and anyone well-versed in data security. They work together to gather the requested information, make sure it’s accurate, and ensure the response aligns with the regulations.
IT and Tech Wizards
DSARs are all about data, and who knows data better than your IT and tech folks? They’re the ones who dig into your systems and databases to find the requested information. From tracking down personal data to ensuring it’s securely delivered, these wizards play an essential role in the DSAR process.
Your Customer Support
Sometimes, DSARs can feel overwhelming for customers. They might need guidance or clarification on the process. That’s where your customer support team steps in. They’re the friendly faces who answer questions, provide updates, and make sure your customers feel supported throughout the DSAR process.
Business Owner or Yourself
If you run a small online venture or a one-person business, chances are you’re the first or even the only point of contact for most communications, including DSARs. In the early stages of a business, it’s quite normal for the owner to handle these requests.
PRO TIP: Set up regular meetings or communication channels between different departments involved in the DSAR process. Effective collaboration ensures a cohesive response and minimizes misunderstandings.
How Long Do You Have to Respond to a DSAR?
According to the GDPR, businesses have to respond to a data request within 30 days from the time the request is received. On the other hand, the CCPA gives businesses 45 days to respond to a DSAR, and they can get another 45-day extension when reasonably necessary.
Once you receive a valid request, the timer starts ticking for responding to the request. However, keep in mind that these timeframes can vary based on specific regulations and local laws.
Some DSARs might involve a massive amount of data, complicated requests, or complex scenarios. If you need more time than the standard timeframe, let the requester know. Keep them informed about the progress and expected response date. This level of communication shows that you’re taking their request seriously.
While time matters when it comes to DSARs, it doesn’t mean you should rush through the process. Responding to a DSAR requires diligence. You need to locate, verify, and compile the requested information accurately. After all, you want to provide comprehensive and correct information to your customers.
PRO TIP: Create a simple system or spreadsheet to track DSAR requests and their deadlines. This ensures you stay organized and never miss a response timeframe.
Can You Refuse to Respond to a DSAR?
Refusing a DSAR is possible under certain circumstances. These may include unreasonable requests, legal privileges, third-party data considerations, and protection of trade secrets. However, while the idea of refusing might be appealing, it’s not straightforward.
While the goal is transparency, there are certain situations where you can legitimately refuse a request. These situations typically deal with specific legal provisions, such as the following:
- Unreasonable Requests: If a person submits excessive requests or makes a request that is vague or repetitious, you might have grounds to refuse.
- Legal Privileges: Sometimes, legal privileges might apply and prevent you from disclosing certain information. This could be the case if the data requested is subject to attorney-client privilege or legal proceedings.
- Third-Party Data: If the DSAR involves revealing someone else’s personal data, you’ll need to tread carefully. Balancing the rights of both requesters and third parties can be tricky, so legal advice might be essential.
- Protection of Trade Secrets: If disclosing certain data could expose sensitive business information or trade secrets, you might be able to refuse. However, you’ll need to demonstrate that the refusal is legitimate and well-founded.
Refusing a DSAR isn’t a decision to be taken lightly. It’s a delicate balance between safeguarding legal rights and ensuring transparency. If you do decide to refuse, communicate your reasons clearly to the requester. Transparency and open communication remain key, even in cases of refusal.
When the grounds for refusal are complex, it’s wise to consult legal experts who specialize in data privacy laws. They can help you determine whether you have valid reasons to refuse and guide you through the process.
PRO TIP: If you decide to refuse a DSAR, make sure to document your decision-making process and reasons for refusal thoroughly. This documentation can be valuable in case of any disputes or legal challenges, helping you demonstrate the legitimacy of your decision.
How to Correctly Respond to a DSAR?
The DSAR response process isn’t just about sending over requested data; it’s a mix of transparency, privacy, and accuracy. Let me walk you through each step of the response process that complies with the DSAR requirements, so you can be prepared to handle it correctly and effectively.
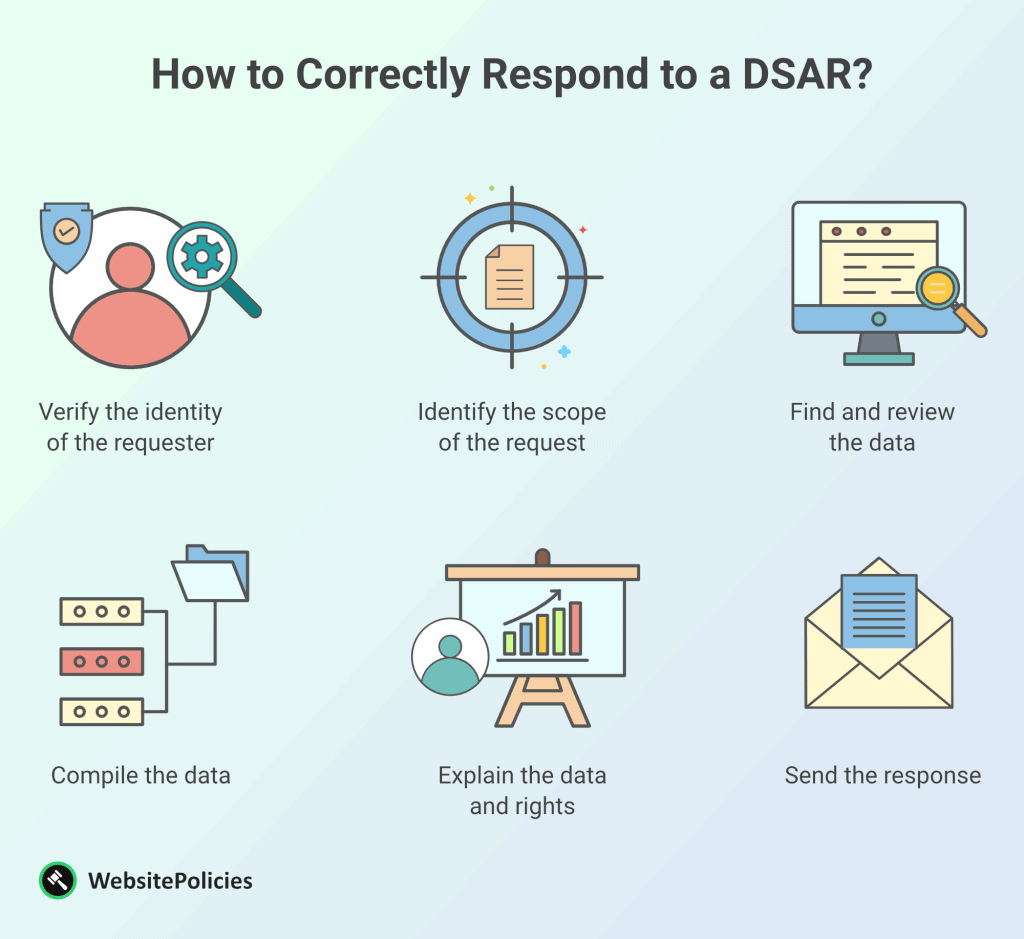
Verify the Identity of the Requester
Upon receipt of the request and before you go into the DSAR process, make sure you’re dealing with the right individual to avoid a potential data breach. Verify the requester’s identity to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. This could involve requesting additional identification documents or utilizing secure communication channels.
Identify the Scope of the Request
To provide a relevant and targeted response, understand the scope of the requester’s inquiry. Clarify the exact information they’re seeking and any specific parameters they’ve outlined. By having a clear understanding of their intentions, you can avoid providing unnecessary data and streamline the response process.
Find and Review the Data
Now, it’s time to play detective. Navigate your systems, databases, and records to locate the data requested in the DSAR. Once you’ve found it, thoroughly review the information to ensure its accuracy and relevance. This step is important in providing precise and trustworthy data to the requester.
Compile the Data
With the data in hand, organize it coherently. You might need to collate information from various sources to create a comprehensive response. Structuring the data in a logical manner ensures that the requester can easily understand the information you’re sharing.
Explain the Data and Their Rights
Data might be second nature to you, but it can be overwhelming for the requester. Provide explanations for the data you’re sharing and break down any technical terms or complex details. This helps them understand its purpose and usage. Additionally, inform them about their rights under data protection laws and how they can further manage their data.
Send the Response
With the data compiled and explanations ready, create your response. Ensure it’s concise, transparent, easily comprehensible, and presented in a user-friendly format. When transmitting the response, use secure communication channels to maintain data privacy and prevent any unauthorized access.
Do You Need to Provide Everything if Requested?
No, you’re not obliged to share everything. While transparency is key, focus on relevant data to fulfill the request while respecting the privacy of others and legal privileges. This means avoiding oversharing unrelated or excessive data.
Let third-party privacy, legal exceptions, and related laws guide your approach. If certain data can’t be shared, communicate clearly and transparently. It’s all about balance and compliance.
Certain data might also be protected by legal privileges or exceptions. For instance, attorney-client communication might be off-limits for disclosure. Similarly, disclosing trade secrets could be detrimental. It’s essential to understand these exceptions and act within the boundaries of the law.
Also, consider familiarizing yourself with regulations for DSAR responses, such as GDPR and CCPA, to ensure you’re on the right track. Remember, data privacy laws should guide your actions.
If you find yourself in a situation where you can’t provide certain information, don’t leave the requester in the dark. Clearly explain the reasons for your decision. Again, transparency in your response, even if it’s a refusal, is important for maintaining trust.
ALSO READ: The Definitive Guide to Privacy Policy
DSAR Response Challenges
Responding to DSARs isn’t always a walk in the park. Several challenges can pop up along the way and make the process a bit of a puzzle. Here are some of the common challenges you might encounter while dealing with DSARs.
- Complex Data Landscapes: Data is stored in different places – databases, cloud services, spreadsheets, you name it. Finding and compiling requested data from these diverse sources can be like piecing together a jigsaw puzzle.
- Large Volume and Scale: Large organizations often deal with mountains of data. When a DSAR comes knocking, sifting through this data to extract the relevant information can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
- Data Accuracy Issues: Data isn’t always perfect. Errors, outdated information, and duplicates can make things unclear.
- Third-Party Data: DSARs might involve data from multiple individuals – not just the requester. Balancing the rights and privacy concerns of these third parties while providing relevant information can be a tricky tightrope to walk.
- Technical Demands: Locating, extracting, and formatting data might require technical know-how. If you’re not well-versed in these areas, navigating systems, databases, and IT infrastructure can pose challenges.
- Meeting Timelines: Data protection laws often set strict timelines for DSAR responses. Making sure you meet these deadlines while also being accurate and thorough in your response can be a juggling act.
While DSARs protect individuals, they can also present some difficulties for businesses. You can streamline the process of submitting requests by using a DSAR form. Besides compliance, it’ll make it easier for your customers and for yourself to review requests.
PRO TIP: Regularly organize and categorize your data sources. Efficient data management practices can simplify the process of locating and compiling requested data when DSARs arise.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a DSAR?
A DSAR (Data Subject Access Request) is when a customer asks a business to provide them with their personal data details to either review, modify, or delete it.
Who can submit a DSAR?
Any individual whose personal data your organization handles can submit a DSAR. It’s a way for them to access and review the information you have about them.
Can a DSAR be refused?
Yes, there are situations where you can legally refuse a DSAR. These could include cases where the request is unreasonable or if specific legal privileges apply.
How long do I have to respond to a DSAR?
Typically, you have around 30 to respond to a data subject once you receive such a request, but the exact timeframe varies depending on the specific data protection laws in your jurisdiction.
What if the data is incorrect?
If the requested data is incorrect or outdated, you should correct it before responding to the DSAR.
Can I charge for a DSAR?
In most cases, you are not allowed to charge a fee for a DSAR. However, there might be exceptions depending on the applicable data protection laws and the nature of the request.
How to ensure data accuracy?
Before responding to a DSAR, it’s essential to double-check the accuracy of the data you provide. This ensures that the information you share is correct and up-to-date.
Do I need a DPO?
Whether you need a Data Protection Officer (DPO) depends on legal requirements and the complexity of your data processing activities. Having a DPO can help ensure proper handling of DSARs and compliance with data protection regulations.



