Every time you visit a website, cookies are used to track user activities and collect data essential for functionalities like maintaining items in your shopping cart.
Primarily, these tiny data files help provide a better user experience by remembering preferences and settings. But not all cookies are the same.
Cookies come in two main types: first-party and third-party.
First-party cookies are created by the site you are visiting directly. In contrast, third-party cookies are generated by external services or ads on that site.
Below, I’ll help you understand the distinctions between first-party cookies vs third-party cookies so you can enhance how your website interacts with your visitors.
- Using first-party cookies, you can personalize the user experience and gather valuable data to improve your website and marketing.
- Web browsers are prioritizing user privacy by blocking third-party cookies. This means you’ll need to focus on collecting your own data (first-party cookies) to understand your audience.
- The future is cookieless, but not data-less. With new methods like contextual advertising, you can still reach your target audience.
Table of Contents
PRO TIP: Don’t waste your time and take the guesswork out of the legal jargon with this personalized cookie policy generator trusted by over 200,000 businesses.
What Are First-Party Cookies?
First-party cookies are small text files a website stores on a user’s device. When a user visits a website, first-party cookies are created and used to track these interactions. They gather first-party data essential for website functionality.
Websites use first-party cookies to enhance the user experience by maintaining session states and personal settings.
For example, they can remember language settings, ensuring the website appears in your preferred language each time you visit.
Businesses then leverage first-party user data to improve site performance and deliver personalized content. Examples of first-party cookies include:
- Session cookies
- Persistent cookies
- Secure cookies
- Performance cookies
First-party cookies boost site functionality and user experience by storing preferences and session data. They are essential for personalized, efficient web interactions.
What Are Third-Party Cookies?
Third-party cookies are a piece of code placed on a user’s device by a website other than the domain the user is visiting. They gather data used by different entities to understand user behavior on various sites.
Third-party cookies are created and are primarily used for tracking and advertising purposes. For example, they help an advertiser deliver more relevant ads to users by providing insights into their browsing habits and preferences.
Examples of third-party services that leave cookies include:
- Ad-retargeting services: These services use third-party cookies to follow users across the internet, showing ads relevant to previously visited websites.
- Analytics companies: These companies gather third-party data on user interaction across multiple sites to help businesses understand consumer behavior and optimize their strategies.
- Social media platforms: These platforms use cookies to track users on and off their sites for advertising and site functionality, like enabling “like” and “share” buttons.
Some of the most common third-party cookies are:
- Advertising cookies
- Tracking cookies
- Analytics cookies
Third-party cookies collect extensive data via a third-party server. They enhance ad relevance and market analysis by linking user activity across multiple sites.
First-Party Cookies vs Third-Party Cookies
As an online business owner, understanding the subtle yet significant differences between the types of cookies you use can greatly impact how you engage with your customers and shape your marketing strategies.
But to truly understand what’s the difference between a first-party vs third-party cookie, you need to look at several points of comparison:
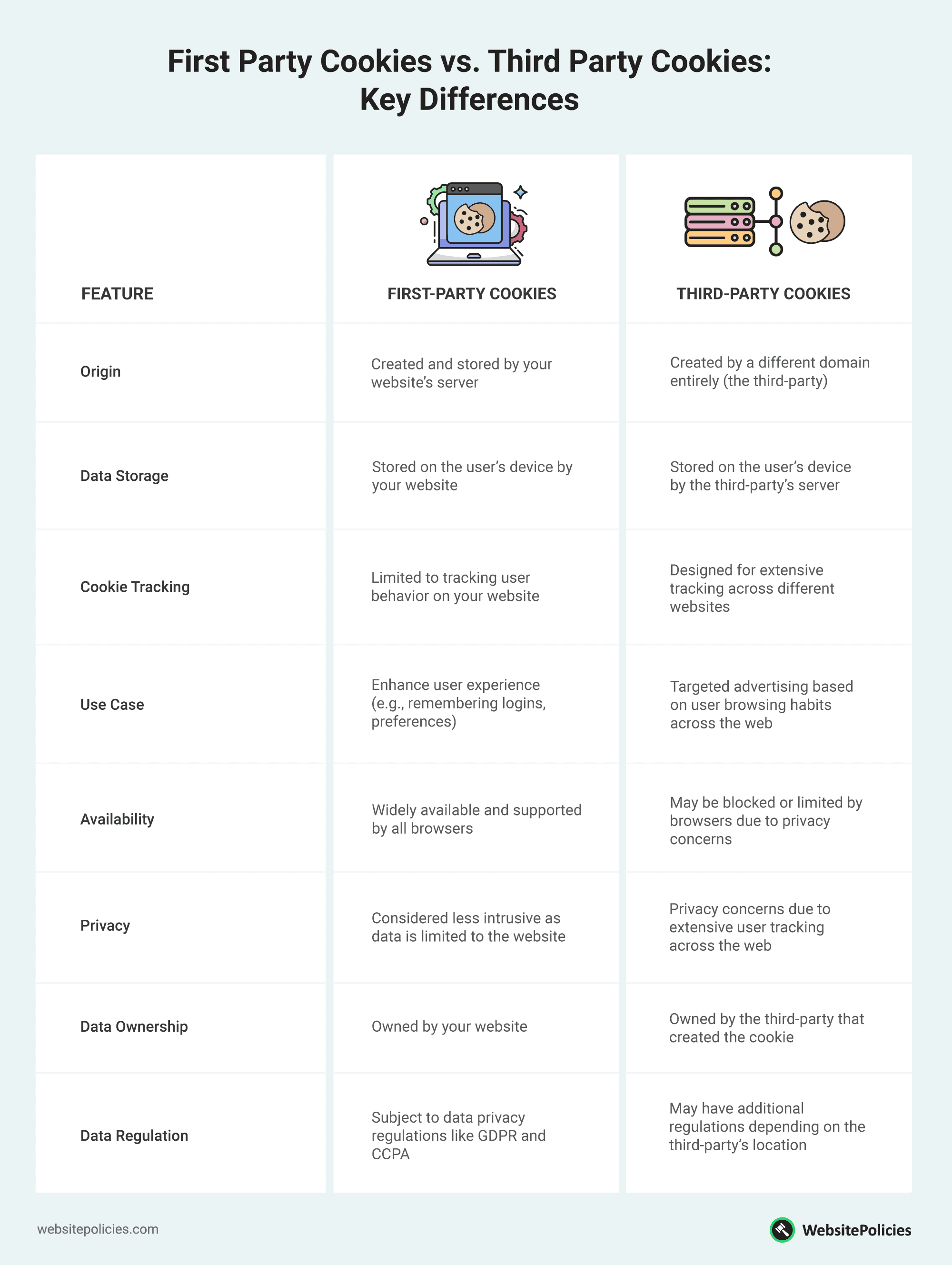
Origin
First-party cookies are stored directly by the web server of the site you own and operate. These cookies are specific to and directly managed by your website.
Conversely, third-party cookies come from a different domain or a different website than the one the user is currently visiting. These are typically set by marketing companies or ad networks.
Privacy and Tracking
When it comes to privacy and tracking, first-party cookies offer a more contained approach to data collection. They directly correlate to your website’s functionality and user enhancements.
In contrast, cookie tracking via third-party sources involves monitoring user behavior across multiple websites. This contributes to more comprehensive user profiles for targeted advertising.
Purpose
Primarily, first-party cookies enhance user experience by maintaining session details, preferences, and other site-specific functionalities.
On the other hand, third-party cookies are extensively used in marketing strategies. They focus more on delivering personalized advertising content across various platforms.
PRO TIP: To build trust with users, be transparent about cookie use. In your cookie policy, clearly explain how cookies enhance their browsing experience.
Storage and Access
First-party cookies stored by your site are only accessible by your domain, ensuring that the data remains under your control.
In the case of third-party cookies, the cookies aren’t confined to just one site. They are accessible by any participating entity within the ad network.
Duration
First-party cookies remain on the user’s device for an extended period to facilitate a consistent and personalized user experience on subsequent visits.
As for third-party cookies, despite also having the potential for long-term storage, regulatory pressures, and evolving privacy standards are leading to a decline in their use and acceptance.
First- and Third-party cookies play distinct roles. First-party cookies enhance site functionality, while third-party cookies broaden ad targeting.
To help you understand the difference between first-party and third-party cookies even more, here’s a table outlining their key differences:
Examples of First-Party Cookies
First-party cookies serve as the backbone for many core functionalities that improve the user experience directly on your site.
Here are three common examples of first-party cookies and how they typically function:
Session Cookies
These cookies are important for users to maintain a continuous browsing session. They enable users to remain logged in as they navigate a site, without needing to re-enter their login details on every page.
For example, session cookies are used to keep items in a shopping cart during a session. They ensure the cart remains populated even as the user adds items from different pages.
Persistent Cookies
Unlike session cookies, persistent cookies remain on the user’s device between sessions. These cookies can be used to remember user preferences and settings, such as theme choices or language settings, for future visits.
A practical scenario is a website remembering a user’s preferred layout or text size, which enhances accessibility and personalization.
Secure Cookies
These cookies are used specifically for security purposes. They ensure that any data exchanged between the web server and the user is transmitted over secure connections.
Secure cookies are essential for eCommerce sites, where secure transactions and the protection of personal and payment information are crucial. They help prevent unauthorized access to user data during transactions.
Examples of Third-Party Cookies
Third-party cookies allow businesses to engage with users more effectively by understanding their interests and habits across the internet.
Here are three examples of third-party cookies and their common uses:
Advertising Cookies
These cookies track user activity across various sites to build a profile of their interests. This helps in serving targeted ads that are more likely to be of interest to the user.
For instance, if a user has been browsing various travel sites, advertising cookies can help travel agencies present deals and promotions on flights and accommodations that appear on different websites the user visits later.
Tracking Cookies
Tracking cookies help companies analyze the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns by tracking user responses and interactions across multiple sites.
For example, a marketing firm can use these cookies to see how often a user sees an ad before clicking on it. This provides valuable insights into ad performance and user engagement.
Analytics Cookies
These cookies are generally employed by third-party analytics services like Google Analytics. They help website owners understand how visitors interact with their sites.
They collect information such as the number of visitors, pages visited, and time spent on pages. This data is invaluable for optimizing site content and layout to improve user experience and site performance.
Do Second-Party Cookies Exist?
Yes, second-party cookies do exist, though they are less commonly discussed than first or third-party cookies. Second-party data refers to information shared directly between two parties involved in a business transaction or partnership.
Unlike first-party cookies, which are created and used solely by the host domain, or third-party cookies generated by a different domain, second-party cookies involve a direct exchange of data originally collected as first-party data by one entity and then shared with another.
Second-party cookies may contain the same information as first-party cookies, but the real difference is in how the data is obtained and used.
Instead of a website collecting data directly from its users, second-party cookies involve one party purchasing or otherwise acquiring that data directly from another party who originally collected it.
This exchange allows businesses to expand their understanding of customers with data they couldn’t collect on their own.
For example, a business might agree to share its customer data with a partner company, where both have similar target markets but offer complementary products.
The cookies created from this shared data help each party enhance their marketing strategies. Using this information, they can tailor their offerings to better meet the needs of shared customer bases.
What Will Happen to First-Party and Third-Party Cookies in the Future?
First-party cookies will gain prominence as web browsers like Chrome phase out third-party cookies to enhance user privacy. This shift pushes businesses to focus on alternatives to third-party cookies for user tracking and advertising.
The statistics from this 2021 Statista survey reveal significant insights about American attitudes toward cookie management, which directly relate to the evolving landscape of first-party and third-party cookies:
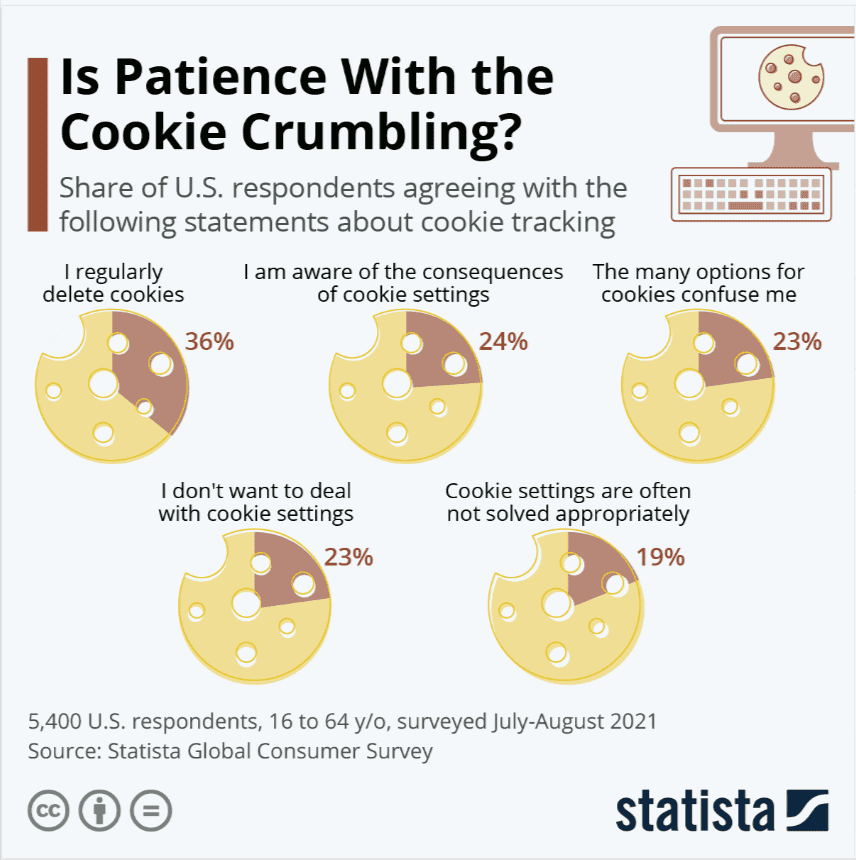
With 36% of respondents regularly deleting cookies and 23% confused by cookie options, it’s clear there’s a growing concern about privacy and a desire for simpler, more transparent control measures.
A more recent survey in April 2023 found that 46% out of 2,000 respondents were concerned about companies tracking their online activities.
What does it mean for you?
As cookie deprecation continues, online businesses will increasingly rely on first-party cookies, which are deemed safer and more privacy-compliant.
The decline of third-party cookies will also encourage the exploration of new methods, such as contextual advertising and the use of privacy-focused analytics tools.
While third-party cookies may fade away, first-party cookies will remain a valuable tool for online businesses. Start adapting innovative privacy-respecting strategies now.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do first-party cookies benefit my website?
First-party cookies enhance your website by storing user preferences and session data. They provide a more personalized and efficient user experience.
Are first-party cookies compliant with GDPR and CCPA?
Yes, first-party cookies are compliant with GDPR and CCPA as long as you clearly inform users and obtain their consent.
Do browsers block first-party cookies?
Typically, browsers like Safari do not block first-party cookies as they are essential for website functionality. Users can choose to block them manually.
What is the impact of blocking third-party cookies in my marketing strategies?
Blocking third-party cookies requires shifting focus to first-party data and alternative methods like contextual advertising for effective marketing.
How can my business adapt to the decline of third-party cookies?
Your business can adapt by focusing on collecting first-party data, using contextual advertising, and leveraging privacy-focused analytics tools.
How can I ensure my website’s cookie practices are transparent to users?
Ensure transparency by clearly explaining your cookie usage in your cookie policy and obtaining user consent before storing cookies.



