The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU law that requires businesses to be transparent about their data practices. To do this, companies need privacy policies that meet GDPR requirements.
But what is the GDPR privacy policy?
A GDPR privacy policy is a legal document that outlines how your business will collect and process personal data. It outlines the type of data you collect, why you use it, and most importantly, how users can control it.
With a comprehensive privacy policy, you show your customers that their personal information is handled with care and respect. This will help make your business more trustworthy and keep you on the right side of data privacy laws around the world.
To make sure yours is compliant, we’ll list what a privacy policy should include, and where it should be displayed, along with a free sample template and examples.
- Having a GDPR privacy policy is crucial for your online business, especially if you serve customers in the EU.
- Your policy should clearly explain what data you collect, why you use it, and how users can control their information. Make sure it’s easy to find on your website and mobile app.
- Inform users of their GDPR rights, including access, correction, and deletion of their data. Provide clear instructions on how to exercise these rights.
Table of Contents
PRO TIP: Take the hassle of writing your own privacy policy away with our privacy policy generator trusted by over 200,000 businesses. It’ll save you hours of work and possible costly legal mistakes.
Free GDPR Privacy Policy Template for Your Website
Understanding the complexities of GDPR compliance requires work, but with the right tools, it’s manageable. To simplify the process for you, check out our sample GDPR privacy policy template below.

This template is designed to help your company’s privacy policy meet GDPR’s transparency requirements. It includes all the necessary sections, from data collection and usage to user rights and data protection measures.
A Better Way to Create a GDPR-Compliant Privacy Policy
If the thought of reading legal documents stresses you out, let alone writing one, consider using a professional privacy policy generator. This tool can create a compliant policy for your website with ease.
It will automatically compile all the necessary elements based on your specific needs and keep it updated with the constantly changing laws, so you don’t have to worry.
PRO TIP: If you’re still worried, you may have a lawyer review the generated policy for added peace of mind. This option is far less expensive and time-consuming than having a lawyer draft it from scratch.
Why Do You Need a GDPR Privacy Policy on Your Website?
You need a GDPR privacy policy on your website because it is a legal requirement for businesses that collect and process the personal data of EU citizens.
This policy serves as a direct line of transparency to your users, informing them of their privacy rights and how they are protected.
This isn’t limited just to companies within the EU. Any business that engages with EU citizens’ data, regardless of location, must comply with the GDPR.
Moreover, having a GDPR privacy policy on your website isn’t just about legal compliance. It also serves to build trust with your customers.
A 2023 survey found that 25% of global organizations consider complying with privacy laws a key factor in building trust.
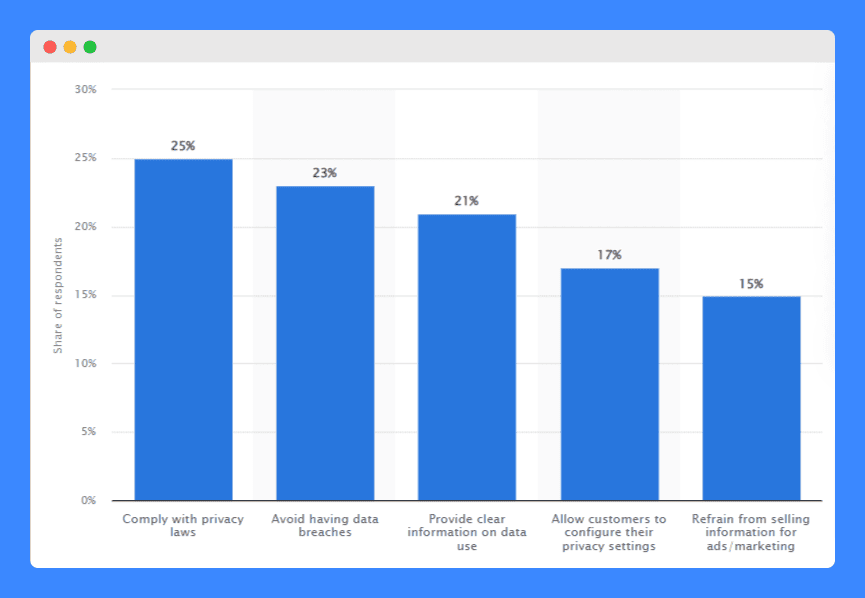
A policy that incorporates these elements demonstrates your commitment to user privacy and aligns with the data privacy expectations of a growing number of consumers worldwide.
12 Key Components of a GDPR-Compliant Privacy Policy
Ensuring compliance with the GDPR isn’t just a legal obligation. It is a commitment to your users’ privacy and security. Here are the key components you should include in your privacy policy to meet GDPR privacy policy requirements:
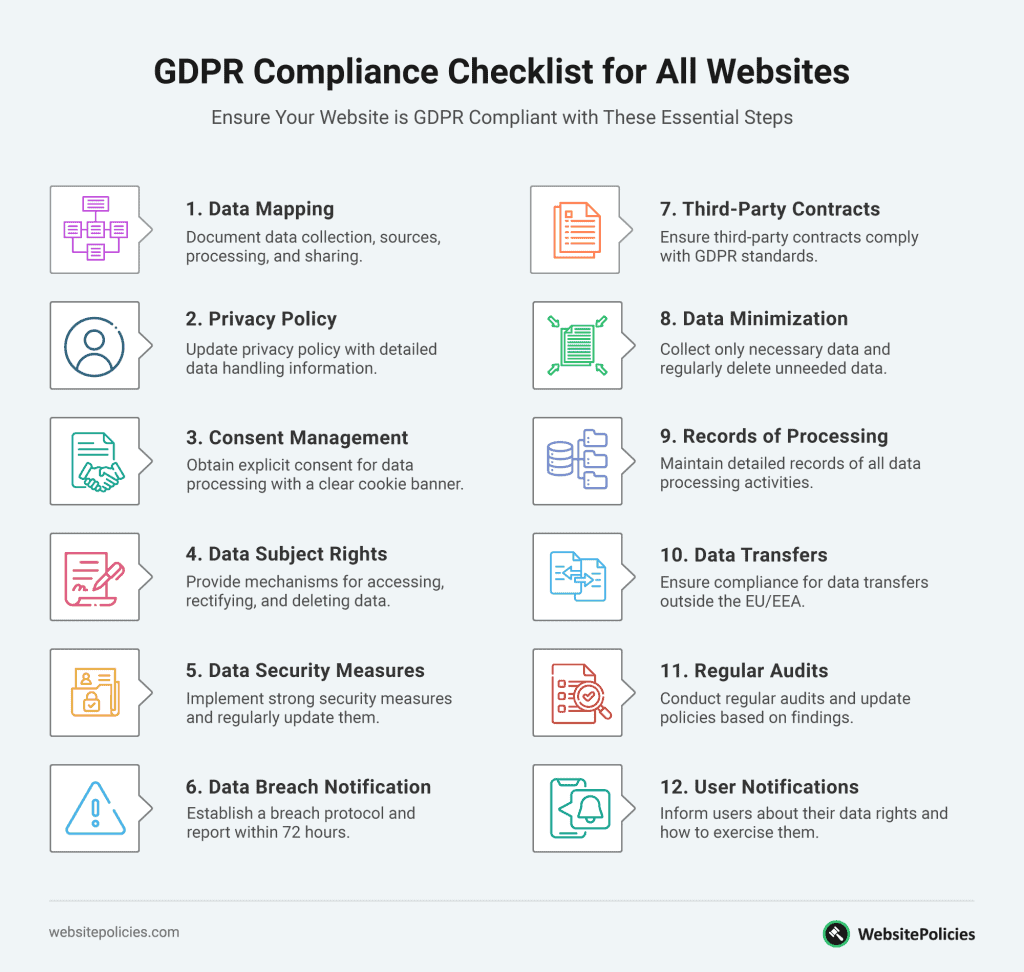
1. Data Mapping
Ensuring GDPR compliance starts with understanding what personal data you collect, why you collect data, and how you use it. This is where data mapping comes in.
Data mapping is a comprehensive process that involves documenting the entire journey of the personal data you collect from your users. It should include details about:
- What data is collected: This includes any information that can be used to directly or indirectly identify an individual, such as names, email addresses, IP addresses, browsing activity, and purchase history.
- Sources of the data: Identify where the data is collected from. This could be through website forms, user accounts, social media logins, or cookies.
- Legal basis for processing: Explain why you need to collect and process this data. The GDPR requires a lawful basis for processing, such as consent from the user, a contractual necessity, or a legitimate interest of your business.
- How the data is processed: Document all the ways you use the collected data. This could include tasks like analyzing user behavior, sending marketing communications, or fulfilling orders.
- Data sharing practices: If you share user data with any third-party vendors or service providers, you need to document who they are and for what purpose the data is shared.
By creating a data map, you gain a clear picture of your data lifecycle and how personal information flows within your organization.
2. Transparent Privacy Policy
Under the GDPR, businesses are required to provide clear and detailed information about how they handle personal data.
This means your privacy policy must be easily accessible, written in plain language, and regularly updated to reflect any changes in your data practices.
Data protection authorities can impose fines for non-compliance with the GDPR. However, a well-drafted privacy policy can help you avoid these penalties by demonstrating a good faith effort to inform users about their data.
3. Consent Management
Consent management involves ensuring that users are fully informed about how their data will be used and providing them with the ability to grant or withhold consent. An effective way to achieve this is through a clear cookie banner.
Lifestyle brand Hill House Home does this effectively in its GDPR-compliant privacy notice:

Their cookie banner offers users a straightforward way to give their explicit consent before they process data. Users have the option to accept or decline cookies.
PRO TIP: Make sure users are able to change their preferences at any time. Pre-ticked checkboxes are also not allowed under GDPR.
4. Data Subject Rights
Enumerate the rights of the data subject, including access, rectification, erasure, and the right to object to data processing. This reaffirms your commitment to user rights under the GDPR.
For example, under Section 9 of Stanley’s Privacy Policy page, you’ll find this:

Here, they list the rights of users as set by the GDPR, as well as how they can exercise these rights. They also include important information about other privacy laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
PRO TIP: Don’t just list the rights. Explain them in a clear and understandable way, and provide instructions on how they can exercise these rights.
5. Data Security Measures
The GDPR places a strong emphasis on the security of personal data. This means website owners have a responsibility to implement and maintain appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect user information.
As the website owner, you are responsible for the security of the data you collect, even if it’s processed by a third-party vendor. Besides, users are more likely to share personal data directly with businesses that demonstrate a commitment to data security.
6. Data Breach Notification
Businesses are required to report a data breach to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours. The report should include the nature of the breach, the categories and number of affected individuals, and the potential consequences of the breach.
In your privacy policy, outline the steps to take immediately after discovering a breach, including containment, assessment, and mitigation measures. It should also specify the roles and responsibilities of team members involved in the response.
PRO TIP: Assign a data protection officer (DPO) to coordinate the response, ensure compliance with reporting requirements, and communicate with the supervisory authority.
7. Third-Party Contracts
When businesses share personal data with third parties, it is essential to establish contracts that outline the responsibilities and obligations of all parties involved in processing the data.
This helps safeguard the data and ensures that third parties adhere to the same high standards of data protection as the primary business.
To ensure GDPR compliance in third-party contracts, consider the following steps:
- Conduct Due Diligence: Conduct thorough due diligence on third parties before entering into a contract. This includes assessing their data protection policies, security measures, and compliance with GDPR requirements.
- Detailed Contracts: The contracts should specify the nature and purpose of data processing, the types of personal data involved, and the duration of processing. They should also outline the security measures that third parties must implement to protect the data.
- Breach Notification: Include provisions requiring third parties to notify the primary business of any data breaches or security incidents without undue delay. This ensures that the primary business can fulfill its own breach notification obligations under the GDPR.
8. Data Minimization
The GDPR emphasizes the principle of data minimization. This means you should only collect the personal data that is absolutely necessary to achieve your legitimate purposes.
There’s a difference between collecting data from users who take specific actions (like making a purchase) and collecting data from all visitors to your website.
Don’t collect data “just in case” you might need it someday. Instead, carefully consider what data you truly need to operate your website and fulfill your business objectives.
For example, to process an order, you might need a customer’s name, billing address, and shipping information. But you likely don’t need their date of birth or political affiliation.
It’s also important that you establish a clear data retention schedule and delete personal data that is no longer necessary for the purposes for which it was collected.
PRO TIP: Use automated tools and processes to facilitate regular data deletion. Set up systems that automatically purge data after a certain period or once it is no longer required.
9. Records of Processing
While not directly included in the privacy policy itself, maintaining detailed records of all data processing activities is a crucial component of GDPR compliance.
These records act as an internal audit trail, documenting what data you collect, why you process it, and where it goes.
For example, this enables you to respond to data subject requests. If a user exercises their GDPR rights (access, rectification, erasure, etc.), you can efficiently locate and manage their data.
It also helps demonstrate compliance. Regulatory authorities may request proof of your GDPR compliance, and these records provide evidence of your data handling practices.
10. Data Transfers
The GDPR requires a privacy policy to address how personal data is protected when transferred internationally.
This is necessary because transferring data to countries outside the EU/EEA that do not have equivalent data protection laws can pose significant risks to the privacy and security of personal information.
To comply, businesses must implement safeguards such as standard contractual clauses, and binding corporate rules, or ensure the destination country has an adequacy decision from the European Commission.
For example, to ease the mind of their site visitors, Windsor added this statement in their privacy policy:

11. Regular Audits
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and so are privacy regulations. Regular audits of your data collection and processing practices are essential for maintaining GDPR compliance.
The audit process can reveal areas where your data practices might not fully align with GDPR requirements. This allows you to take corrective actions and update your privacy policy accordingly.
Privacy laws like the GDPR may be updated over time. Regular audits help you stay informed about changes and adapt your privacy policy to reflect the latest legal requirements.
12. User Notifications
Explaining how users will be notified of any changes in the privacy policy is a crucial component of a GDPR-compliant privacy policy.
To achieve this, businesses should implement clear procedures for notifying users about changes. This can include sending email notifications, displaying prominent announcements on the website, or using in-app messages.
It’s also essential to include a section in the privacy policy that states when the policy was last updated, ensuring transparency and enabling users to review the changes.
Where to Display a GDPR Privacy Policy
Ensuring that your GDPR privacy policy is easily accessible is crucial for compliance and for maintaining transparency. Here’s where and how you should display your privacy policy across different platforms:
Website
Including a link to your privacy policy in the footer ensures it is accessible from every page of your website. This placement is standard practice and helps maintain transparency with site visitors, showing that your business takes privacy seriously.
Mobile App
For mobile apps, the GDPR privacy notice should be easily accessible through the app’s settings menu or within the user account section.
It’s also a good practice to present the privacy policy during the initial app setup or registration process, where users are most likely to review it.
When sending emails, especially those that collect personal data for newsletters or promotions, include a link to your privacy policy in the footer of the email.
This practice ensures recipients understand how their data will be handled right from the point of interaction.
GDPR-Compliant Privacy Policy Examples You Can Learn From
Creating a GDPR-compliant privacy policy that effectively communicates your data protection principles is vital for maintaining transparency with your users.
To help you better understand what makes an effective privacy policy, let’s explore some examples that exemplify strong compliance and clear communication.
1. Brooklinen
Brooklinen’s Privacy Policy serves as an excellent sample privacy policy for several reasons, especially in its clear articulation of rights for European residents under GDPR.
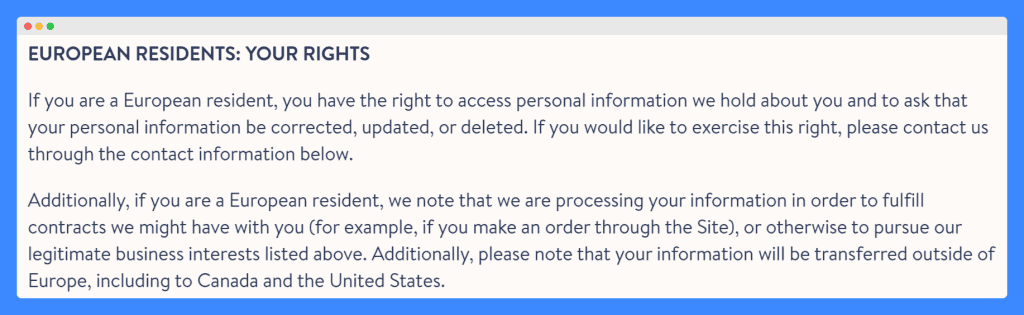
For one, it straightforwardly informs European residents of their rights to access, correct, update, or delete their personal information. This is crucial for compliance with GDPR, emphasizing the importance of clear communication regarding data subject rights.
It also explicitly states the purpose behind the processing of personal data, such as fulfilling contracts or pursuing legitimate business interests. This clarity meets GDPR’s mandate that organizations must clearly disclose why they process personal data.
2. Petal + Pup
Petal + Pup’s approach exemplifies what constitutes a good privacy policy by addressing key GDPR considerations while also accommodating global privacy expectations.
It acknowledges that privacy rights can vary by location but commits to making reasonable efforts to honor requests universally:

This inclusivity not only enhances the policy’s global applicability but also builds a strong trust foundation with a diverse international audience.
Plus, providing a direct link for users to submit requests for access or deletion of their personal information simplifies the process. The alternative contact method for such requests also ensures users have multiple avenues to exercise their rights.
3. Faherty
Faherty’s privacy policy serves as a good example of GDPR compliance primarily because it transparently addresses the issue of international data transfers—a key concern under GDPR.
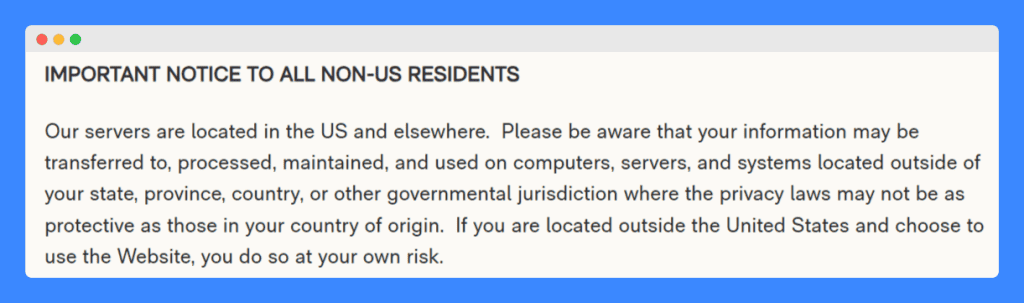
The policy informs users that data protection laws in other countries might not be as stringent as in their home country. This sets user expectations and manages potential risks associated with data transfer.
4. Ridge
In this sample GDPR privacy policy from Ridge, you can see how it specifically tailors information to meet the stringent requirements of the GDPR.
This section of the policy details the types of data processed, processing purposes, recipient categories, and additional necessary information, all of which align with GDPR transparency requirements.
Furthermore, it informs users about their rights, including the right to object and the procedures to exercise these rights.
5. Vegamour
Vegamour’s section for EU residents makes it a strong GDPR privacy policy example. By explicitly mentioning the ability to withdraw consent and providing a direct contact method for requests, it ensures transparency and user empowerment.

It also includes a practical guide on how to lodge a complaint with the data protection authority in several jurisdictions, which not only helps users address concerns locally but also demonstrates compliance with GDPR’s requirement to inform users of their legal rights.
The inclusion of specific rights such as access, correction, deletion, and portability further aligns with GDPR mandates, making this policy a comprehensive blueprint for respecting user data privacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who does the GDPR apply to?
The GDPR applies to any entity that processes the personal data of EU residents. It’s vital to follow this policy if you’re handling such data.
How do I update my existing privacy policy to comply with the GDPR?
Review your privacy policy for GDPR requirements. Update it to include data processing details and user rights.
How often should you update your GDPR-compliant privacy policy?
Update your GDPR-compliant privacy policy whenever there are changes in data practices. Regularly review for any changes to your privacy policy.
How do I get consent from my users under GDPR?
Under GDPR, explicit consent must be obtained via clear opt-in methods. Ensure the consent request is specific and informed.
What is the penalty for non-compliance with GDPR?
Penalties for GDPR non-compliance can reach up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover. The fine depends on the severity of the breach.



