f you are a website owner that regularly produces original and unique content, you have no doubt toyed with the idea of using Google AdSense.
And the more traffic you have on your website, the more participating in Google AdSense’s program makes sense as this means more people seeing and clicking on those ads.
Blogs, forums, and websites offering any kind of free tools all have great potential for generating revenues with AdSense as they are generally high-traffic websites that are free to use, which means that users won’t mind seeing an ad or two.
However, as we will see below, Google AdSense has some requirements that you must comply with to get your application approved and keep your account in good standing.
Table of Contents
PRO TIP: Take the hassle of writing your own privacy policy away with our privacy policy generator trusted by over 200,000 businesses. It’ll save you hours of work and possible costly legal mistakes.
What is Google AdSense?
If you have ever visited a website and seen ads for third-party websites and products, chances are they have been generated by Google AdSense.
This program allows website owners to monetize their platforms by allowing advertisers to bid for space on their page. Google then delivers targeted and relevant ads to your audience and, in return, you get compensated based on the number of people that engage with or view those ads.
In order to deliver personalized ads, Google uses cookies that gather information about website visitors, such as their general location and previous websites visited. This is why you will often see ads for a product or brand that you just browsed on an unrelated third-party website. This is a great remarketing tool for advertisers.
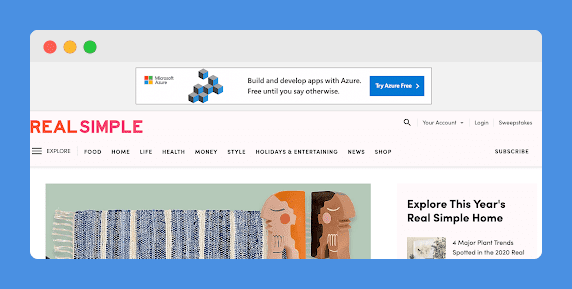
Here is an example from Real Simple’s website, a high-traffic lifestyle magazine. That ad for Microsoft Azure that is placed in the header would have been generated by AdSense.
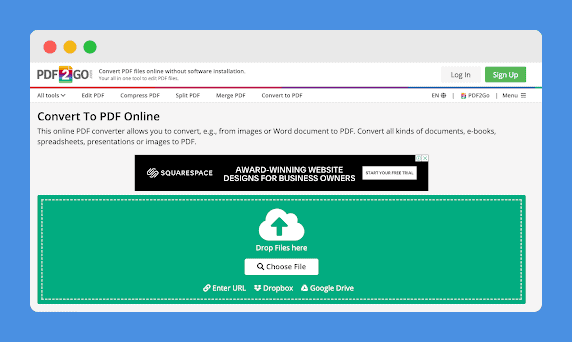
And here is an example from the website PDF2GO, a tool that allows users to convert files to PDF format free of charge. In exchange, visitors are served with ads, like the one in the header from Squarespace.
AdSense is fairly easy to set up, one must simply have a Google account, add a piece of code to their website, choose where they would like the ads to appear (ad placements) and Google takes care of the rest.
How Much Can You Earn From Google AdSense?
It all depends on the ad, as they are paid for by the advertisers themselves who bid for the ad space.
You will be paid on a pay-per-click or on a pay-per-impression basis, depending on the type of ad. For that reason, this amount will vary significantly depending on how much traffic you get on your website, how many ads appear on your page, the type of content that you share, and, of course, your users, their behavior, and where they are located.
You can strategically select ad placements to maximize the number of impressions and clicks and, thus, your earnings.
Bloggers will often place AdSense ads within a piece of content, as the user has to scroll past it to continue reading the article.
As seen above in our examples, a website header is also a popular place for banner ads as is the footer. Another common ad placement is in the white space, on the sides of a page; this allows for bigger, vertical ads.
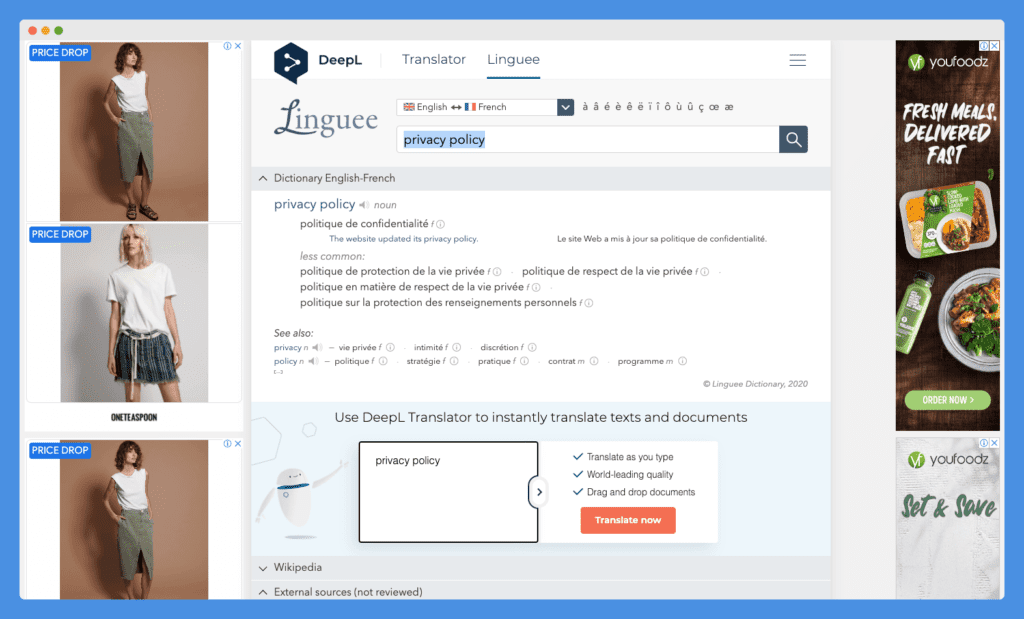
Linguee, a free translation tool, maximizes the white space on both sides of its tool by allowing ad placements:
Google AdSense Requirements
Like most platforms, Google AdSense requires users to agree and comply with its terms and conditions when signing up to use the service.
The exact terms and conditions vary depending on the country where your billing address is located – this is an excerpt from the terms applicable for a United States billing address.
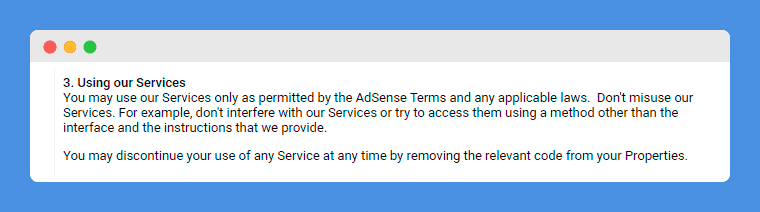
Section 3 of the AdSense Online Terms of Service specifies that a website owner must comply with these terms as well as with any applicable laws in order to be allowed to use AdSense.
Moreover, Section 10 of the AdSense Online Terms of Service sets out the requirement that any website that uses their program must have a clear and easily accessible privacy policy that notably addresses cookies and information stored from users’ devices.
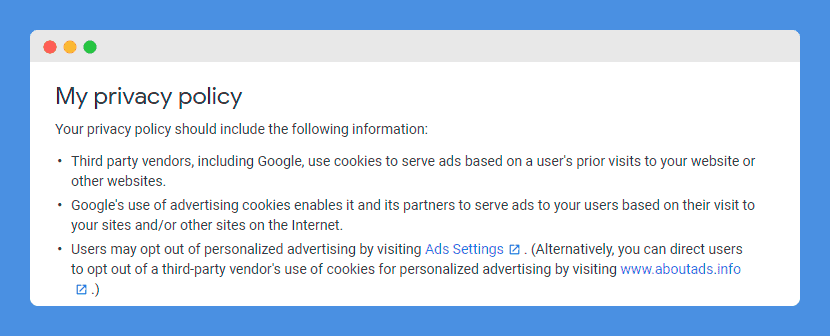
Note that this privacy policy must inform users about their options when it comes to cookie management.
Specifically, when required by law, the website owner must use “commercially reasonable efforts” to ensure that consent was given by the user in regards to storing and accessing their cookies, device-specific information, location, or other information on their device.
In other words, your privacy policy must have a cookie component and comply with applicable laws, which notably includes the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Online Privacy Protection Act (CalOPPA).
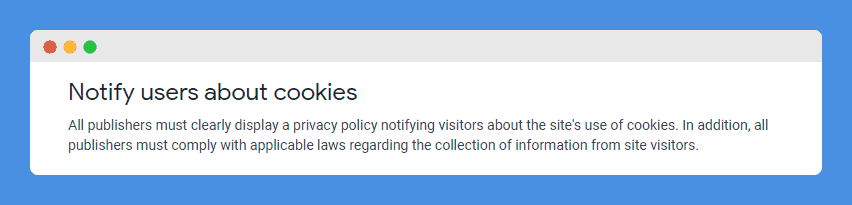
Indeed, as mentioned earlier, Google places and stores a cookie on a user’s browser when they click on or visit a page that includes ad tags or displays Google ads (and anytime an activity results in a call to their servers).
These cookies allow Google to serve users with personalized and more relevant ads and to avoid showing someone the same ads over and over again.
EEA and UK Website Visitors
In that regards, Google requires that you comply with its EU User Consent Policy if using any of their products (including AdSense), which implies making certain disclosures to and requesting consent from users located in the European Economic Area (EEA) and the United Kingdom in regards to your use of cookies and the collection, sharing, and use of personal data required for ads personalization.
As websites generally do not exclude people from specific countries from visiting their page, there is a chance that you will have users from the European Economic Area and the United Kingdom, so you should keep this in mind.
Here is a screenshot of the EU User Consent Policy which aims to ensure compliance with the GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive:

In other words, you must obtain your users’ consent to the use of cookies and the collection of their personal data which may be shared and used to serve them with targeted ads.
To comply with this policy, you must also retain records of their consent and make it easy for your users to revoke it by providing them with instructions on how to do so. You must also clearly identify each party with whom data will be shared.
This is in line with applicable European data privacy laws, notably the GDPR, which are known as the strictest on the planet.
Essential Elements in a Privacy Policy for Google AdSense
The exact contents of your privacy policy could vary depending on the nature of your website and the data that you collect.
However, Google does provide some guidance to website owners when it comes to what should be included in their privacy policies, all the while reminding them that applicable laws vary from one country to the other.
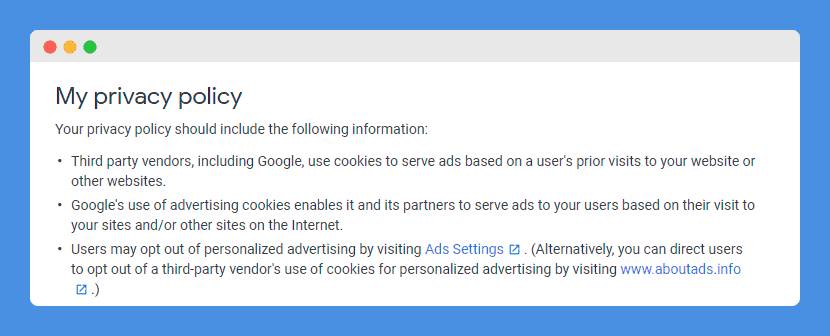
Your privacy policy should set out which types of cookies you use, including third-party cookies, the reasons why you are using them, and how your users can opt-out of cookie collection.
If you are allowing Google to serve ads from third-party vendors or ad networks that place cookies on your website you will need to notify your users and name those third-party vendors as well as links to their websites where your users can manage cookies.
At a minimum, you should direct your users to the internetcookies.com website for information on how to manage cookies.
If you have a separate cookie policy that addresses all of the above, you could include it in your privacy policy or link to it directly – as long as both policies are easily accessible and clear, and understandable to your users, which is necessary in order to comply with article 12 of the GDPR.
We know how complicated this can seem, which is why we have created a privacy policy generator that provides you with a policy that meets Google AdSense’s requirements (as well as many other services) and uses the strictest guidelines to provide you with global coverage.
Privacy Policy for Google AdSense Examples
Major British online fashion retailer Asos has an extensive section on its website that addresses privacy and cookies.
It is a great example of a website owner using clear, user-friendly language and taking into account that Asos’ target demographic is between the ages of 18 and 34 years old – they even have a short 53 seconds video to better engage with their users.
This page is long, but here is a screenshot from the “how we use your information” section:
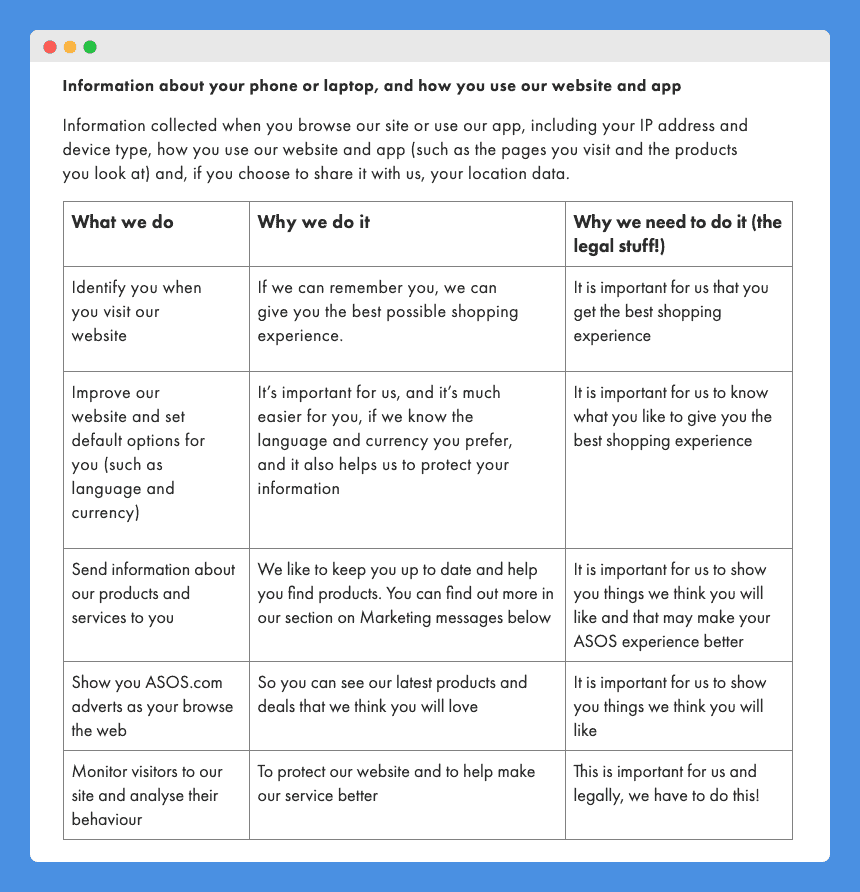
It also addresses how and with which third parties Asos shares users’ information:

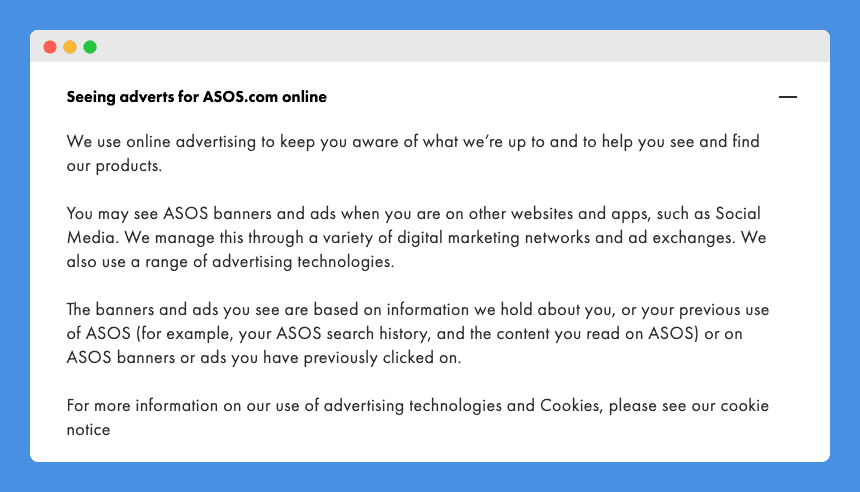
Since most of their customers are located in Europe, Asos lists out in its privacy policy all the rights that users have in regards to their personal information and provide the contact details of their data protection officer, which is required by the GDPR.
Asos refers to its cookie notice in its privacy policy and includes a direct link to it. Their cookie policy explains the types of cookies used by the online retailer and how it uses the data collected:

Another good example is the information and entertainment network CBS. The company has a whole section dedicated to privacy on its website, including a page that specifically addresses personalized advertising and how to limit or disable it:

This is in addition to CBS’ privacy policy and cookie policy which set out the types of cookies used to automatically collect information.
Cookie Consent Banners
To ensure your compliance with Google’s terms and conditions as well as with the GDPR, you could use a cookie banner or pop-up to request your website users’ affirmative consent to the use of cookies (such as by having them check a box or clicking “I agree”, for example);
This will allow you to ensure that you have a lawful basis to process their data under article 6(1)(a) of the GDPR and retain a record of that consent (the text, options, and the date and time when the user consented).
Cookie banners appear on most websites nowadays – they are usually placed at the bottom of a page and pop-up to ask you to click and register your consent before you can proceed to navigate a website.
Here is the cookie banner that appears when you visit AirBnB’s website:
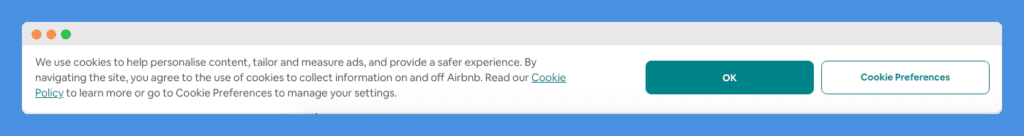
It informs users that AirBnB uses cookies and allows them to either accept by clicking OK or navigate to “Cookie Preferences” to learn more about the type of cookies that they use and to manage or revoke permission.
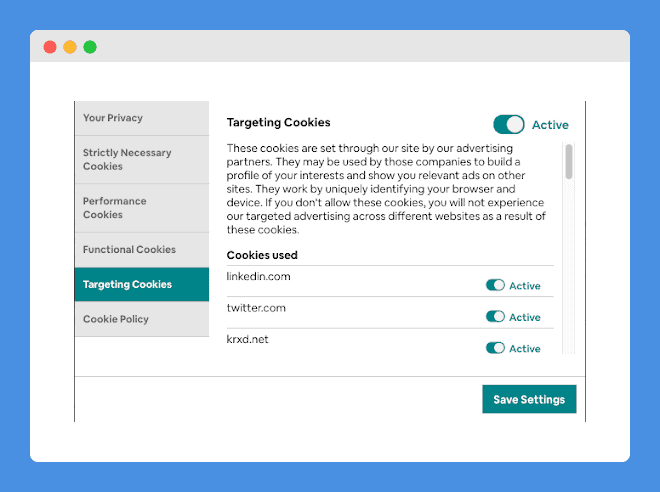
Here is a screenshot of the “Cookies Preferences” pop-up which also links to the Cookie Policy:
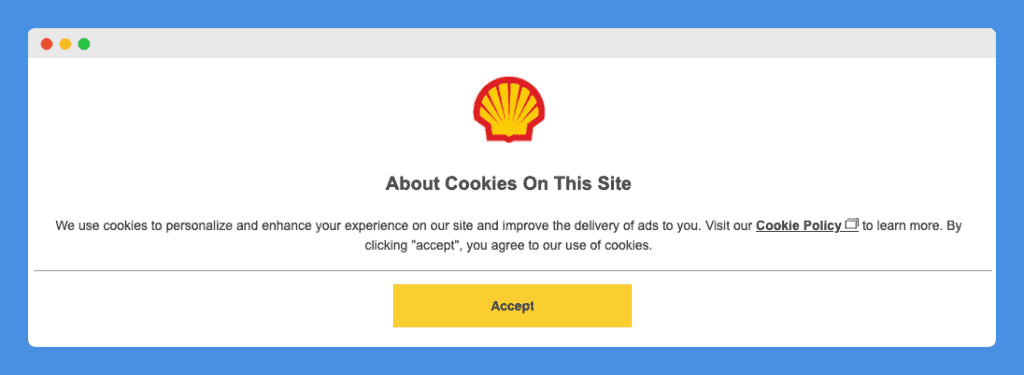
Another example is Shell’s website; when a user lands on the homepage a full-screen pop-up appears:
These are just examples and the guidelines provided by Google are just that, guidelines.
What Happens if You Apply to or Use AdSense Without a Privacy Policy?
Google actively monitors websites that use AdSense from a user’s perspective to ensure that they remain compliant with their Program Policies, which includes the EU User Content Policy, when applicable.
If you are found to be non-compliant and thus violating their terms of service, Google can disable or suspend your account by not serving ads to your website – effectively removing a source of passive income for your business and potentially preventing you from further participating in Google’s AdSense program.
Many other Google services require a valid privacy policy, including Google Analytics and Google Maps – with users located all over the globe, ensuring that you have a legally compliant and easy-to-understand policy in place is primordial.
And wanting to comply with Google’s terms of use is not the only reason why you should have a privacy policy on your website.
Notwithstanding the legal aspects of it, having a transparent privacy policy contributes to building a relationship of trust with your users and should be considered best practice for any website owner.



